5060. Reverse
Polish notation
Reverse Polish notation (RPN) is a mathematical
notation in which every operator follows all of its operands. It is also known
as postfix notation and does not need any parentheses as long as each operator
has a fixed number of operands.
For example:
·
the
expression 2 + 4 in RPN is represented like 2 4 +
·
the
expression 2 * 4 + 8 in RPN is represented like 2 4 * 8 +
·
the
expression 2 * (4 + 8) in RPN is represented like 2 4 8 + *
Evaluate the value of an arithmetic expression in
Reverse Polish Notation. Valid operators are +, -, *, /. Operator / is an
integer division (14 / 3 = 4). Each operand may be an integer or another
expression.
Input. One line contains expression written in Reverse Polish
notation. The length of expression is no more than 100 symbols.
Output. Print the value of expression given in Reverse Polish
notation.
|
Sample input 1 |
Sample output 1 |
|
2 4 * 8 + |
16 |
|
|
|
|
Sample input 2 |
Sample output 2 |
|
2 4 8 + * |
24 |
SOLUTION
stack
Algorithm
analysis
Let’s partition the input expression into terms, which
are the number or one of the four operators. The terms will be processed as
follows:
·
if term is
a number, push it into stack;
·
if term is
an operator, extract two numbers from
the stack, perform the operation and push the result into stack.
When the expression is processed, the stack contains
one number that is the result of calculations.
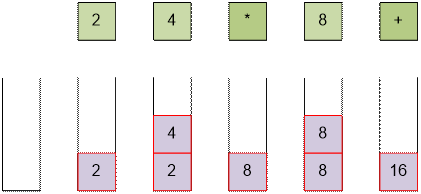
Example
The
expression “2 4 * 8 +” is equivalent to “2 * 4 + 8”.
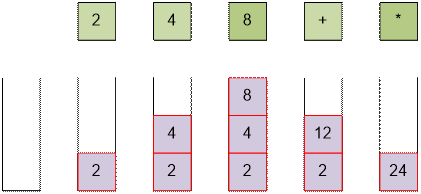
The
expression “2 4 8 + *” is equivalent to “2 * (4 + 8)”.
Algorithm
realization
Declare the working array and the stack.
char s[200];
stack<int>
st;
Read the terms till the end of expression, sequentially
processing them.
while(scanf("%s",s)
== 1)
{
Process four arithmetic operations.
if (s[0] == '+')
{
a = st.top(); st.pop();
b = st.top(); st.pop();
st.push(a+b);
} else
if (s[0] == '-')
{
a = st.top(); st.pop();
b = st.top(); st.pop();
st.push(b-a);
} else
if (s[0] == '*')
{
a = st.top(); st.pop();
b = st.top(); st.pop();
st.push(a*b);
} else
if (s[0] == '/')
{
a = st.top(); st.pop();
b = st.top(); st.pop();
st.push(b/a);
} else
Term val is a number. Transform it from the char
array into variable val and push into
the stack.
{
sscanf(s,"%d",&val);
st.push(val);
}
}
Print the result of expression that is on the top of
the stack.
printf("%d\n",st.top());
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
Stack<Integer> st = new
Stack<Integer>();
while(con.hasNext())
{
String s = con.next();
if (s.equals("+"))
{
Integer a = st.pop();
Integer b = st.pop();
st.push(a + b);
} else
if (s.equals("-"))
{
Integer a = st.pop();
Integer b = st.pop();
st.push(b - a);
} else
if (s.equals("*"))
{
Integer a = st.pop();
Integer b = st.pop();
st.push(a*b);
} else
if (s.equals("/"))
{
Integer a = st.pop();
Integer b = st.pop();
st.push(b/a);
} else
st.push(Integer.parseInt(s));
}
System.out.println(st.peek());
con.close();
}
}
Python realization
Read the inpt string, the expression in Reverse Polish
notation.
lst = input().split()
Declare the stack s.
s = []
Process sequentially the terms till the end of the list
lst.
for v in lst:
Process four arithmetic operations.
if v == '+':
a = s.pop()
b = s.pop()
s.append(a + b)
elif v == '-':
a = s.pop()
b = s.pop()
s.append(b - a)
elif v == '*':
a = s.pop()
b = s.pop()
s.append(a * b)
elif v == '/':
a = s.pop()
b = s.pop()
s.append(b // a)
else:
Term v is a number. Transform it from the string
representation into the number and push into the stack.
s.append(int(v))
Print the result of expression that is on the top of
the stack.
print(s.pop())